Explanation of Osteopathy
Based on a health-oriented medical philosophy, osteopathic medicine uses a number of concepts to implement its principles. The neuromusculoskeletal system is used as a common point of reference because it directly relates the individual to the physical environment on a day-to-day basis. The practitioner’s primary roles are to:
- Address primary cause(s) of disease using available evidence- based practices
- Enhance the patient’s healing capacity
- Individualize patient management plans with an emphasis on health restoration and disease prevention
- Use palpatory diagnosis and manipulative treatment to focus on and affect somatic signs of altered structural, mechanical, and physiologic states
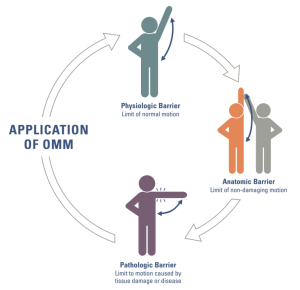 Osteopathic philosophy is meant to guide osteopathic physi- cians in the best use of scientific knowledge to optimize health and diminish disease processes. Upon founding his profession and school, Still expressed the hope that “the osteopath will take up the subject and travel a few miles farther toward the fountain of this great source of knowledge and apply the results to the relief and comfort of the afflicted who come for counsel and advice” (14). It is the intention of the authors to organize current medical knowledge and place it on a foundation of osteopathic philosophy. We do this in order to provide the osteopathic medical student with a road map that will lead to the further study of the science of osteopathy and the practice of the highest quality patient-centered health care possible.
Osteopathic philosophy is meant to guide osteopathic physi- cians in the best use of scientific knowledge to optimize health and diminish disease processes. Upon founding his profession and school, Still expressed the hope that “the osteopath will take up the subject and travel a few miles farther toward the fountain of this great source of knowledge and apply the results to the relief and comfort of the afflicted who come for counsel and advice” (14). It is the intention of the authors to organize current medical knowledge and place it on a foundation of osteopathic philosophy. We do this in order to provide the osteopathic medical student with a road map that will lead to the further study of the science of osteopathy and the practice of the highest quality patient-centered health care possible.
Osteopathic manipulative medicine (OMM) is a core set of techniques of osteopathy and osteopathic medicine distinguishing these fields from mainstream medicine
40 different OMM techniques
- Active Method
- Articulatory Technique
- Balanced Ligamentous Tension
- Chapman Reflex
- Combined Method
- Compression of the Fourth Ventricle
- Counterstrain
- Direct Method
- Exaggeration Method
- Exaggeration Technique
- Facilitated Oscillatory Release Technique
- Facilitated Positional Release
- Fascial Unwinding
- Functional Method
- Hepatic Pump
- High Velocity/Low Amplitude Technique
- Indirect Method
- Inhibitory Pressure Technique
- Integrated Neuromusculoskeletal Release
- Ligamentous Articular Strain
- Lymphatic Pump
- Mandibular Drainage Technique
- Mesenteric Release Technique
- Muscle Energy
- Myofascial Release
- Myotension
- Osteopathic Cranial Manipulative Medicine
- Passive Method
- Pedal Pump
- Percussion Vibrator Technique
- Positional Technique
- Progressive Inhibition of Neuromuscular Structures
- Range of Motion Technique
- Soft Tissue Technique
- Still Technique
- Thoracic Pump
- Toggle Technique
- Traction Technique
- V-Spread Technique
- Visceral Manipulation